publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order.
2025
-
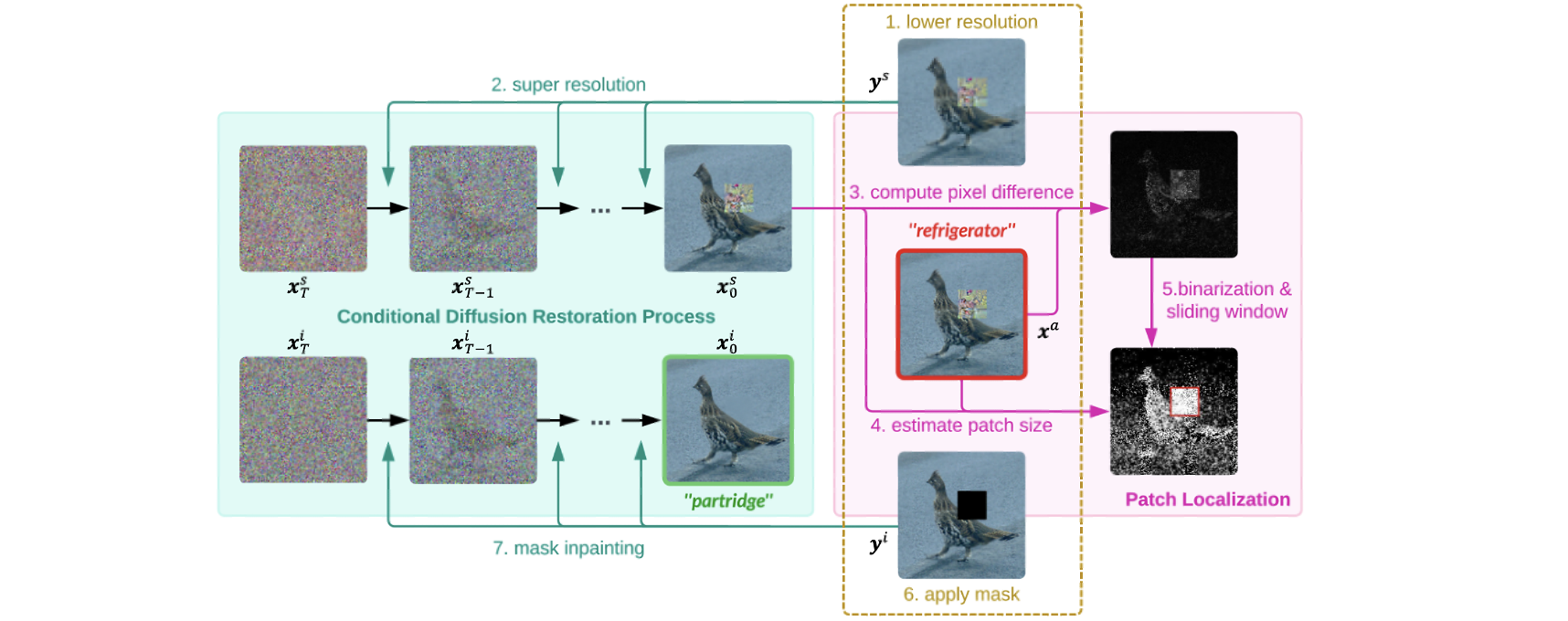 DiffPAD: Denoising diffusion-based adversarial patch decontaminationFu, J., Zhang, X., Pashami, S., Rahimian, F., and Holst, A.In IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Tuscon, Arizona, USA, Feb 2025
DiffPAD: Denoising diffusion-based adversarial patch decontaminationFu, J., Zhang, X., Pashami, S., Rahimian, F., and Holst, A.In IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Tuscon, Arizona, USA, Feb 2025In the ever-evolving adversarial machine learning landscape, developing effective defenses against patch attacks has become a critical challenge, necessitating reliable solutions to safeguard real-world AI systems. Although diffusion models have shown remarkable capacity in image synthesis and have been recently utilized to counter l_p-norm bounded attacks, their potential in mitigating localized patch attacks remains largely underexplored. In this work, we propose DiffPAD, a novel framework that harnesses the power of diffusion models for adversarial patch decontamination. DiffPAD first performs super-resolution restoration on downsampled input images, then adopts binarization, dynamic thresholding scheme and sliding window for effective localization of adversarial patches. Such a design is inspired by the theoretically derived correlation between patch size and diffusion restoration error that is generalized across diverse patch attack scenarios. Finally, DiffPAD applies inpainting techniques to the original input images with the estimated patch region being masked. By integrating closed-form solutions for super-resolution restoration and image inpainting into the conditional reverse sampling process of a pre-trained diffusion model, DiffPAD obviates the need for text guidance or fine-tuning. Through comprehensive experiments, we demonstrate that DiffPAD not only achieves state-of-the-art adversarial robustness against patch attacks but also excels in recovering naturalistic images without patch remnants. The source code is available at https://github.com/JasonFu1998/DiffPAD.
2024
-
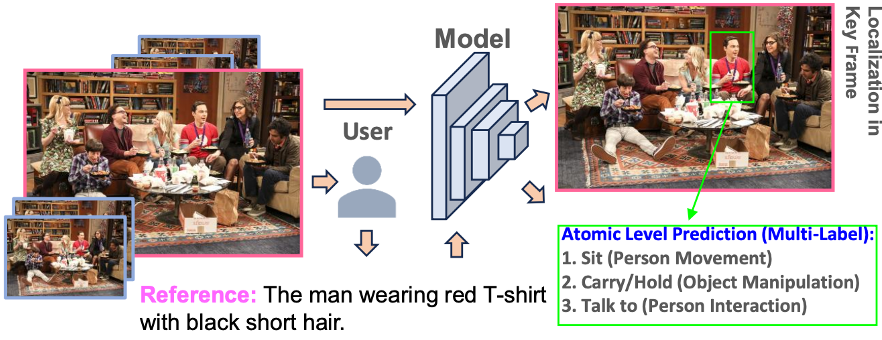 Referring atomic video action recognitionPeng, K.*, Fu, J.*, Yang, K., Wen, D., Chen, Y., Liu, R., Zheng, J., Zhang, J., Sarfraz, M., Stiefelhagen, R., and Roitberg, A.In European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, Oct 2024 (* indicates shared first author)
Referring atomic video action recognitionPeng, K.*, Fu, J.*, Yang, K., Wen, D., Chen, Y., Liu, R., Zheng, J., Zhang, J., Sarfraz, M., Stiefelhagen, R., and Roitberg, A.In European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, Oct 2024 (* indicates shared first author)We introduce a new task called Referring Atomic Video Action Recognition (RAVAR), aimed at identifying atomic actions of a particular person based on a textual description and the video data of this person. This task differs from traditional action recognition and localization, where predictions are delivered for all present individuals. In contrast, we focus on recognizing the correct atomic action of a specific individual, guided by text. To explore this task, we present the RefAVA dataset, containing 36,630 instances with manually annotated textual descriptions of the individuals. To establish a strong initial benchmark, we implement and validate baselines from various domains, e.g., atomic action localization, video question answering, and text-video retrieval. Since these existing methods underperform on RAVAR, we introduce RefAtomNet – a novel cross-stream attention-driven method specialized for the unique challenges of RAVAR: the need to interpret a textual referring expression for the targeted individual, utilize this reference to guide the spatial localization and harvest the prediction of the atomic actions for the referring person. The key ingredients are: (1) a multi-stream architecture that connects video, text, and a new location-semantic stream, and (2) cross-stream agent attention fusion and agent token fusion which amplify the most relevant information across these streams and consistently surpasses standard attention-based fusion on RAVAR. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of RefAtomNet and its building blocks for recognizing the action of the described individual. The dataset and code are publicly available at https://github.com/KPeng9510/RAVAR.
-
 Advancing open-set domain generalization using evidential bi-level hardest domain schedulerPeng, K., Wen, D., Yang, K., Luo, A., Chen, Y., Fu, J., Sarfraz, M., Roitberg, A., and Stiefelhagen, R.In Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, Dec 2024
Advancing open-set domain generalization using evidential bi-level hardest domain schedulerPeng, K., Wen, D., Yang, K., Luo, A., Chen, Y., Fu, J., Sarfraz, M., Roitberg, A., and Stiefelhagen, R.In Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, Dec 2024In Open-Set Domain Generalization (OSDG), the model is exposed to both new variations of data appearance (domains) and open-set conditions, where both known and novel categories are present at test time. The challenges of this task arise from the dual need to generalize across diverse domains and accurately quantify category novelty, which is critical for applications in dynamic environments. Recently, meta-learning techniques have demonstrated superior results in OSDG, effectively orchestrating the meta-train and -test tasks by employing varied random categories and predefined domain partition strategies. These approaches prioritize a well-designed training schedule over traditional methods that focus primarily on data augmentation and the enhancement of discriminative feature learning. The prevailing meta-learning models in OSDG typically utilize a predefined sequential domain scheduler to structure data partitions. However, a crucial aspect that remains inadequately explored is the influence brought by strategies of domain schedulers during training. In this paper, we observe that an adaptive domain scheduler benefits more in OSDG compared with prefixed sequential and random domain schedulers. We propose the Evidential Bi-Level Hardest Domain Scheduler (EBiL-HaDS) to achieve an adaptive domain scheduler. This method strategically sequences domains by assessing their reliabilities in utilizing a follower network, trained with confidence scores learned in an evidential manner, regularized by max rebiasing discrepancy, and optimized in a bi-level manner. The results show that our method substantially improves OSDG performance and achieves more discriminative embeddings for both the seen and unseen categories. The source code will be available at https://github.com/KPeng9510/EBiL-HaDS.
2023
-
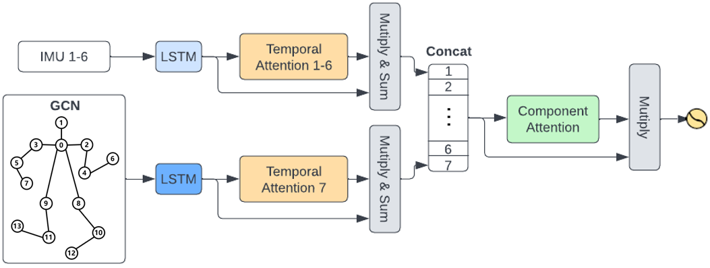 Component attention network for multimodal dance improvisation recognitionFu, J., Tan, J., Yin, W., Pashami, S., and Björkman, M.In ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Paris, France, Oct 2023 (10% Oral Session)
Component attention network for multimodal dance improvisation recognitionFu, J., Tan, J., Yin, W., Pashami, S., and Björkman, M.In ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Paris, France, Oct 2023 (10% Oral Session)Dance improvisation is an active research topic in the arts. Motion analysis of improvised dance can be challenging due to its unique dynamics. Data-driven dance motion analysis, including recognition and generation, is often limited to skeletal data. However, data of other modalities, such as audio, can be recorded and benefit downstream tasks. This paper explores the application and performance of multimodal fusion methods for human motion recognition in the context of dance improvisation. We propose an attention-based model, component attention network (CANet), for multimodal fusion on three levels: 1) feature fusion with CANet, 2) model fusion with CANet and graph convolutional network (GCN), and 3) late fusion with a voting strategy. We conduct thorough experiments to analyze the impact of each modality in different fusion methods and distinguish critical temporal or component features. We show that our proposed model outperforms the two baseline methods, demonstrating its potential for analyzing improvisation in dance.
2019
-
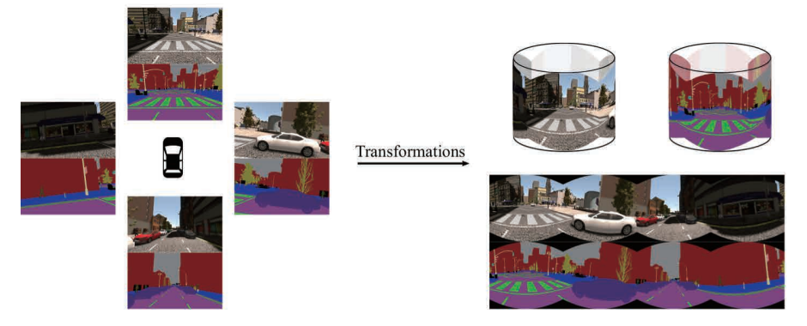 Semantic segmentation of panoramic images using a synthetic datasetXu, Y., Wang, K., Yang, K., Sun, D., and Fu, J.In SPIE Security + Defence Symposium, Strasbourg, France, Sep 2019
Semantic segmentation of panoramic images using a synthetic datasetXu, Y., Wang, K., Yang, K., Sun, D., and Fu, J.In SPIE Security + Defence Symposium, Strasbourg, France, Sep 2019Panoramic images have advantages in information capacity and scene stability due to their large field of view (FoV). In this paper, we propose a method to synthesize a new dataset of panoramic image. We managed to stitch the images taken from different directions into panoramic images, together with their labeled images, to yield the panoramic semantic segmentation dataset denominated as SYNTHIA-PANO. For the purpose of finding out the effect of using panoramic images as training dataset, we designed and performed a comprehensive set of experiments. Experimental results show that using panoramic images as training data is beneficial to the segmentation result. In addition, it has been shown that by using panoramic images with a 180 degree FoV as training data the model has better performance. Furthermore, the model trained with panoramic images also has a better capacity to resist the image distortion. Our codes and SYNTHIA-PANO dataset are available: https://github.com/Francis515/SYNTHIA-PANO.